News
news center
What are the types of couplings?
Release time:
2023-08-26
Coupling refers to a device that connects two shafts or shafts and rotating parts to rotate together in the process of transmitting motion and power, and does not disengage under normal circumstances. Sometimes it is also used as a safety device to prevent the connected parts from bearing excessive load and play the role of overload protection. The coupling is an interface for high-precision connection between the shaft and the shaft.
Coupling is also called coupling. Mechanical components used to firmly couple the driving and driven shafts in different mechanisms to rotate together and transmit motion and torque. Sometimes it is also used to connect shafts with other parts (such as gears, pulleys, etc.). It is often composed of two halves, which are respectively connected with keys or tight fits, fastened to the two shaft ends, and then the two halves are connected in some way. The coupling can be used to compensate the offset (including axial offset, radial offset, angular offset or comprehensive offset) between the two shafts due to inaccurate manufacturing and installation, deformation during work or thermal expansion, and to alleviate impact and absorb vibration.
Most of the commonly used couplings have been standardized or standardized. In general, it is only necessary to correctly select the type of coupling and determine the type and size of the coupling. When necessary, the load capacity of the vulnerable weak links can be checked and calculated. When the rotating speed is high, the centrifugal force of the outer edge and the deformation of the elastic element need to be checked, and the balance check is carried out.
The role of the coupling
Couplings are used to connect shafts in different mechanisms, mainly through rotation, so as to transmit torque. Under the action of high-speed power, the coupling has the function of buffering and damping, and the coupling has a better service life and work efficiency guarantee.
The function of the coupling: a device that connects two shafts or shafts and rotating parts, rotates together in the process of transmitting motion and power, and does not disengage under normal circumstances. Sometimes it is also used as a safety device to prevent the connected parts from bearing excessive load and play the role of overload protection.
The coupling is installed between the driving side and the passive side of the power transmission to transmit rotating torque, compensate for installation deviation between shafts, absorb equipment vibration and buffer load impact. One of the functions of the coupling is to absorb and compensate for the deviation between the shaft and the shaft through its own deformation. The greater the flexibility, the stronger the ability to absorb the deviation; the smaller the flexibility, the weaker the ability to absorb the deviation. Generally speaking, the deviation between the shaft and the shaft is divided into the following three aspects: the connection between the coupling and the peripheral equipment is realized by inserting the shaft of the equipment into the shaft hole of the coupling.
1. The function of the coupling is to connect two shafts (driving shaft and driven shaft) in different mechanisms to rotate together and transmit torque. Some couplings also have the functions of buffering, damping and improving the dynamic performance of the shaft system.
2. Eliminate the inertia of the radial force, the connection between the motor spindle and the load, and use the coupling to weaken the starting force when the motor starts.
3. Power transmission, transmitting power and torque (improving the working performance of the transmission system)
4. Different degrees of vibration reduction and buffering effect
5. When the load is too large, it is disconnected and protected.
6. Good for maintenance
7. Change the transmission direction
8. concentricity correction (varying degrees of axial, radial, angular compensation performance)
What are the types of couplings?
Flexible coupling
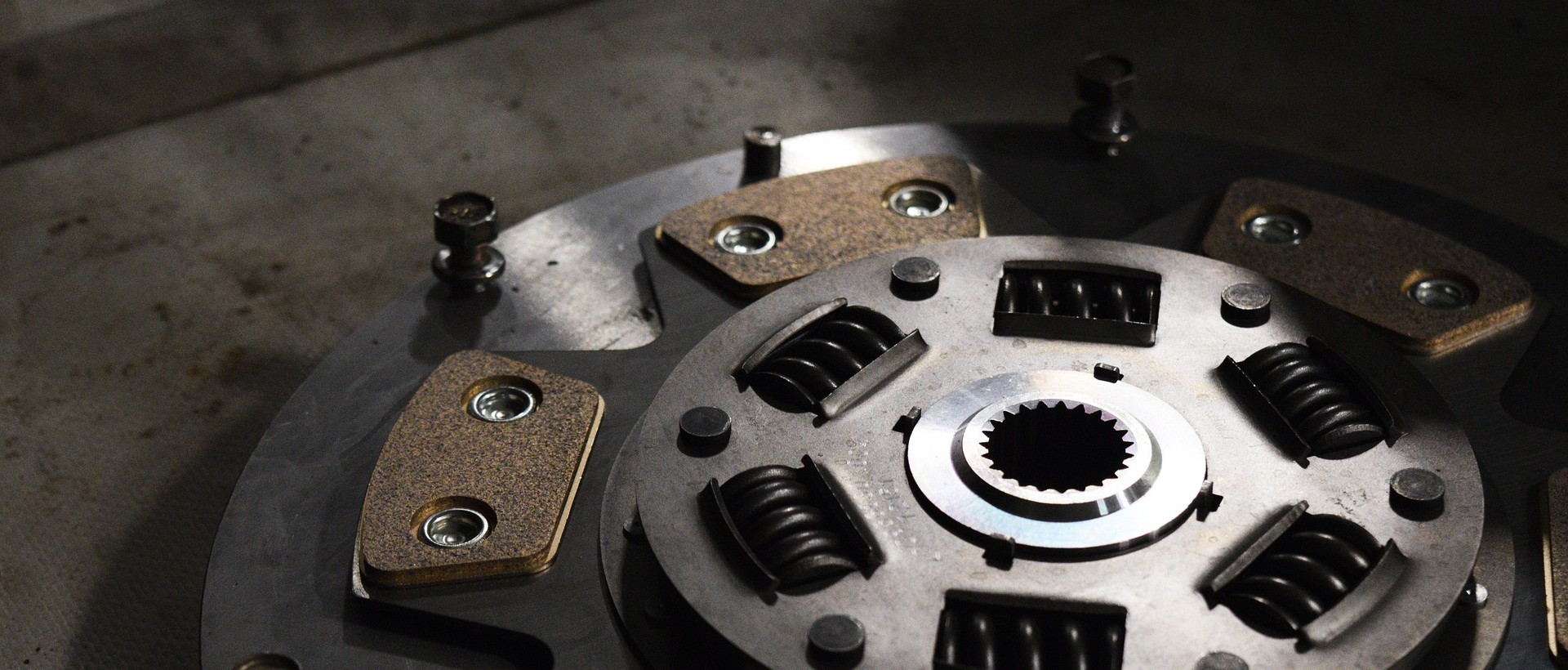
Among the couplings, there is a part that is flexible and deformable. When connecting the two rotating shafts, a certain misalignment of the two rotating shafts is allowed, I .e. a dynamic deformable coupling. The use of flexible couplings will reduce the accuracy requirements of alignment, facilitate testing, and have a good shock absorption function when the speed is unstable. But it has a disadvantage, because its material is rubber, nylon, etc., so it has low strength, short life, small carrying capacity, and is not resistant to high and low temperatures, and is only suitable for low temperature occasions.
1. Plum-blossom coupling
The plum coupling is a widely used coupling, also known as a claw coupling, which consists of two metal claw discs and an elastomer. The two metal claw discs are typically 45 steel, but aluminum alloys are also useful where load sensitivity is required. Its elastomer is usually composed of engineering plastic or rubber. The life of the elastomer is the life of the coupling. The life of the elastomer is 10 years. Since the elastic body has the function of buffering and reducing vibration, it is widely used in the case of strong vibration. The limit temperature of the elastomer determines the use temperature of the coupling, which is usually -35 to 80 degrees.
2. Elastic column coupling
The elastic column coupling is a pin made of some non-metallic elastic material, which is placed in the flange holes of the two half-couplings. Through this pin, two half-couplers can be connected. The structure of the coupling is simple and easy to manufacture. It is convenient to install, remove and replace the elastic element without moving the two couplings.
3. Spring coupling
Spring-loaded couplings transmit motion by welding or connecting a corrugated thin-walled tube directly to the coupling halves. The spring coupling has simple structure, small size, convenient processing and installation, and high transmission accuracy. They are mainly used for low-power precision machinery and control mechanisms that require compact structures and high transmission accuracy.
4. Universal joint coupling
The universal joint coupling uses the characteristics of its mechanism so that the two shafts are not on the same shaft, and there is an angle between the shafts. It can realize continuous rotation of two shafts and reliably transmit torque and motion. The biggest feature of the universal joint coupling is that its structure has a large angle compensation capacity and a compact structure, but compared with other couplings, its transmission efficiency is not very good. The angle between the two shafts of universal joint couplings of different structural types is different, usually between 5-45.
5. Rigid coupling
Rigid coupling, as the name suggests, rigid coupling is actually a torsional rigid coupling. Even under load, there is no turning gap. The rigid coupling is rigid to transmit torque even if there is a load-generating deviation. Rigid couplings are required to connect two shafts in strict alignment without relative misalignment, so they are rarely used in motor test systems. Of course, if the relative displacement can be successfully controlled (the alignment accuracy is high enough), the rigid coupling can also play an excellent role in the application. Especially the small size of the rigid coupling has the advantages of light weight, ultra-low inertia and high sensitivity. In practical application, the rigid coupling has the advantages of maintenance-free, super oil resistance and corrosion resistance.
6. Membrane coupling
Several sets of diaphragms (stainless steel plates) are interlaced with the two half couplings by bolts. Each set of diaphragms consists of multiple components, which are divided into connecting rods and entire diaphragms of different shapes. The membrane coupling compensates the relative displacement of the two axes by elastic deformation of the membrane. It is a high-performance elastic coupling with strong metal elements. It does not require lubrication, compact structure, high strength, long service life, no rotation gap, and is not affected by temperature and oil. It has the characteristics of acid resistance, alkali resistance and corrosion resistance, and is suitable for high performance. The shafting drive has working conditions of temperature, high speed and corrosive media. In terms of structural features, it has an insurance link. When the actual load exceeds the predetermined load, the diaphragm will break, cutting off the movement and power transmission, thereby protecting the rest of the machine from damage and playing a safety protection role.
Hot News

